Did you know that there are over 3 million Americans who have glaucoma right now? The National Eye Institute predicts that the numbers will stand at 4.2 million by 2030.
We’d also like to introduce our newest glaucoma specialist, Dr. Molly M. Walsh, MD, MPH who is a new member of the Boling Vision Center team! Keep reading to learn how you can be aware of glaucoma!
What is Glaucoma?
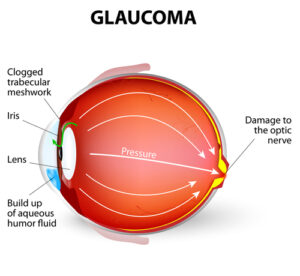
Glaucoma is a progressive group of eye diseases that leads to damage of the optic nerve. This damage to the optic nerve is irreversible, meaning that any vision loss that occurs is permanent.
When left untreated, glaucoma will lead to loss of vision and even blindness.
Your eyes have specialized cells that produce a clear fluid. This clear fluid is the aqueous humor, and it helps to nourish the eyes.
The eyes also have a drainage system that ensures continuous drainage of the aqueous humor. This enables the eye pressure to remain stable.
But when there are issues in the drainage system, such as the drainage system becoming clogged, the result is a buildup of fluid. This leads to an increase in the eye pressure that causes the optic nerve to atrophy.
The optic nerve transmits light signals to the brain. Its damage leads to irreversible vision loss.
In the early stages, a person with glaucoma may not realize they have it as the condition is normally painless and progresses slowly.
Risk Factors of Glaucoma
Because some types of glaucoma can destroy your vision without noticeable symptoms or signs, it’s essential to know the factors that can increase your risk of developing the condition. Common risk factors include:
- Being of Hispanic or African American descent
- Having a family history of glaucoma
- Certain medical conditions like sickle cell anemia, diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease
- Being over the age of 60
- Having increased eye pressure
- Suffering trauma to the eye
- Undergoing some eye surgeries
- Extreme far-sightedness or nearsightedness
- Long-term use of corticosteroids, especially eye drops
Treatment
Glaucoma treatment won’t restore lost vision, but it will prevent further vision loss. Treatment is typically aimed at lowering the intraocular pressure.
This is possible by reducing the amount of fluid produced in your eye or increasing fluid drainage from the eye. Urgent treatment that requires the use of medication and surgery is necessary if you have glaucoma that hasn’t responded to medication.
Medication

Glaucoma treatment begins with eye drops. Some of the commonly prescribed eye drops are alpha-adrenergic agonists, prostaglandins, miotic agents, and beta-blockers.
It’s crucial to take the eye drops exactly as prescribed. Not taking these as your ophthalmologist prescribes them means you may end up with further damage to the optic nerve.
If the eye drops don’t lower your intraocular pressure, your eye doctor may prescribe an oral medication.
Surgery
Surgery becomes necessary if medications are not well tolerated or don’t work as desired. Glaucoma surgery includes:
Minimally invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS)
During MIGS procedures, a small tube is put into the drainage area of the eye. This creates a permanent opening for draining fluid out of your eye.
MIGS procedures are less invasive than traditional glaucoma surgeries, but they are not right for all glaucoma patients. They are often best for patients with mild to moderate glaucoma.
Laser surgery
During a procedure called a selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT), blockages in your eye’s drainage channels are removed and cleared. This leads to lower IOP for patients, sometimes by as much as 30%.
This is often recommended for patients with primary or secondary open-angle glaucoma. SLT produces less scar tissue and for patients that find success with it, they can have it performed again later on.
Drainage implants
With drainage implants, you’ll have a tiny tube placed into your eye. This helps to increase the drainage of fluid from the eye and lowers IOP.
A glaucoma drainage implant may be something that your ophthalmologist at Boling Vision Center recommends if eye drops and previous laser treatments haven’t lowered your intraocular pressure enough. These are also known as tube shunts or an aqueous shunt.
Living with glaucoma
If you have glaucoma, there is no cure so it’s important to find ways to live with it. For many patients, making lifestyle changes can make a big difference.

Exercising regularly
Being active has plenty of benefits but for glaucoma patients, it could help lower your intraocular pressure. It can also help manage risk factors like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Eating a healthy and balanced diet
Eating a healthy diet that consists of nutrients and vitamins A, C, and E can improve your eye health. You may also want to add foods with omega-3 fatty acids to your diet. These include foods like salmon, walnuts, and tuna.
Keep stress to a minimum
Taking care of your emotional and mental health is important. Find healthy ways to reduce stress, as stress has direct links to angle-closure glaucoma.
Limit how much caffeine you drink
Limiting your caffeine intake is highly recommended. High caffeine levels can increase your intraocular pressure.
Don’t smoke
If you’re a smoker, you already know how bad it is for you. But if you’re a smoker with glaucoma, you need to stop smoking immediately.
Smoking can increase your risk of developing cataracts or even dry eye syndrome. If you know that you’re already at an increased risk of developing glaucoma, smoking heightens this risk.
Avoid overexposure to UV rays from the sun
Wearing your hat and sunglasses when outside can help prevent overexposure to sunlight. Too much exposure to the sun’s UV rays can have devastating consequences for your eyes.
Potential Complications of Glaucoma
While the potential complications of glaucoma aren’t life-threatening, untreated glaucoma can result in serious eye complications. You can reduce the risk of complications by seeking medical care promptly.
If you do receive a glaucoma diagnosis, you need to stick to the treatment plan designed by your eye doctor. Possible glaucoma complications include:
- Loss of peripheral or central vision
- Chronic corneal edema (buildup of fluid in the cornea)
- Vision changes
- Loss of vision
The importance of regular appointments and treatment
Loss of vision from glaucoma is usually not obvious until you’ve already lost most of your peripheral vision. This is one of the reasons that glaucoma is often referred to as the secret thief of sight.
The eye doctors at Boling Vision Center recommend frequent eye checks for people over the age of 40. We also recommend routine dilated eye exams by a specialist who can recognize the disease at its earliest stage.
Because glaucoma is a chronic disease, it’s important for our eye doctors to see patients regularly.
Due diligence is extremely important when it comes to keeping glaucoma under control.
When diagnosed early, further vision loss due to glaucoma can be avoided. Wondering if you may need to see a provider for the management and treatment of Glaucoma? Schedule an appointment at Boling Vision Center at one of our four convenient locations in Elkhart, Goshen, or South Bend today!






